Class 8 notes of chp 2 in geography
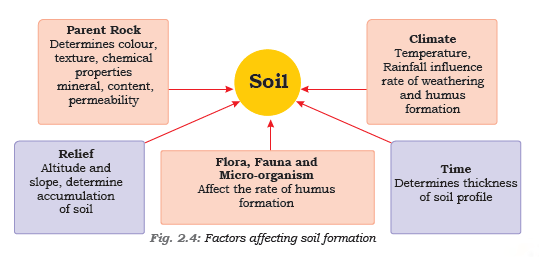
Factors of Soil Formation
- The nature of the parent rock
- Climatic factors
- Topography
- Role of organic material
- Time taken for the composition of soil formation
Degradation of Soil and Conservation Measures
Soil erosion and depletion are the major threats to the soil as a resource. Both human and natural factors can lead to degradation of soils. Factors, which lead to soil degradation are:
- deforestation
- overgrazing
- overuse of chemical fertilizers or pesticides
- rain wash
- landslides and floods
Meanwhile, some methods of soil conservation are given below:
Mulching: The bare ground between plants is covered with a layer of organic matter like straw and it helps to retain soil moisture
Contour barriers: Stones, grass, soil are used to build barriers along contours. Trenches are made in front of the barriers to collect water
Rock dam: Rocks are piled up to slow down the flow of water and also help to prevent gullies and further soil loss
Terrace farming: Broad flat steps or terraces are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops, thus reducing surface runoff and soil erosion
Intercropping: Different crops are grown in alternate rows and are sown at different times to protect the soil from rain wash
Contour ploughing: Ploughing parallel to the contours of a hill slope to form a natural barrier for water to flow down the slope
Shelterbelts: In the coastal and dry regions, rows of trees are planted to check the wind movement to protect soil cover
Water
Three fourth of earth’s surface is covered with a vital renewable natural resource known as water. Oceans covers about 2/3rds of the earth’s surface and supports a rich variety of plant and animal life. However, it is saline and not useful for human consumption. Freshwater accounts for only 2.7% and 70% of these occurs as ice-sheets and glaciers in Antarctica, Greenland and mountain region and they are inaccessible because of their location. Thus, only 1% of freshwater is useful for human consumption.
Water can neither be added nor subtracted from the earth and its total volume remains constant. Its abundance seems to vary only because of the constant motion, cycling through the oceans, the air, the land and back again, through the processes of evaporation, precipitation and run-off. This, as you already know is referred to as the ‘water cycle’.
Problems of Water Availability
Most parts of the world are facing shortages in the freshwater supply. Countries located in climatic zones most susceptible to droughts face great problems of water scarcity. Thus, water shortage may be a consequence of variation in seasonal or annual precipitation or the scarcity is caused by overexploitation and contamination of water sources.
Conservation of Water Resources
To get access to clean and adequate water sources, steps have been taken to preserve this resource:
- Forest and other vegetation cover slow the surface runoff and replenish underground water Water harvesting is another method to save the surface runoff
- The canals used for irrigating field should be properly lined to minimise losses by water seepage
- Sprinklers effectively irrigate the area by checking water losses through seepage and evaporation
- In dry regions with high rates of evaporation, drip or trickle irrigation is very useful
- The valuable water resource can, therefore, be conserved by adopting these means of irrigation
Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Natural vegetation and wildlife exist only in the narrow zone of contact between the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere that we call the biosphere. In the biosphere living beings are interrelated and interdependent on each other for survival. This life-supporting the system is known as the ecosystem. Wildlife includes animals, birds, insects as well as the aquatic life forms. The birds feed on insects and act as decomposers as well. Vulture due to its ability to feed on dead livestock is a scavenger and considered a vital cleanser of the environment. So, animals big or small, all are integral to maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
Distribution of Natural Vegetation
The growth of vegetation depends primarily on temperature and moisture. The major vegetation types of the world are grouped as forests, grasslands, scrubs and tundra.
In areas of heavy rainfall- Huge trees thrive- forests are thus associated with areas having abundant water supply. As the number of moisture decreases- the size of trees and their density reduces-short stunted trees and shrubs grow in regions of moderate rainfall. In dry areas- Thorny shrubs and scrubs grow in low rainfall areas.
Conservation of Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Changes in climate and human interference can cause the loss of natural habitats for the plants and animals. Deforestation, soil erosion, constructional activities, forest fires, tsunami and landslides are some of the human and natural factors that accelerate the process of extinction of these resources. One other major concern is the poaching that results in a sharp decline in the number of particular species. National parks, wildlife sanctuaries, biosphere reserves are made to protect our natural vegetation and wildlife. Conservation of creeks, lakes, and wetlands is necessary to save the precious resource from depletion.
Awareness programmes like social forestry and Vanamohatasava are also established at the regional and community level. School children are also encouraged to bird watch and visit nature camps so that they appreciate the habitat of varied species. Many countries have passed laws against the trade as well as the killing of birds and animals. In India, killing lions, tigers, deers, great Indian bustards and peacocks is illegal. Meanwhile, an international convention CITES has been established that lists several species of animals and birds in which trade is prohibited.

Comments
Post a Comment